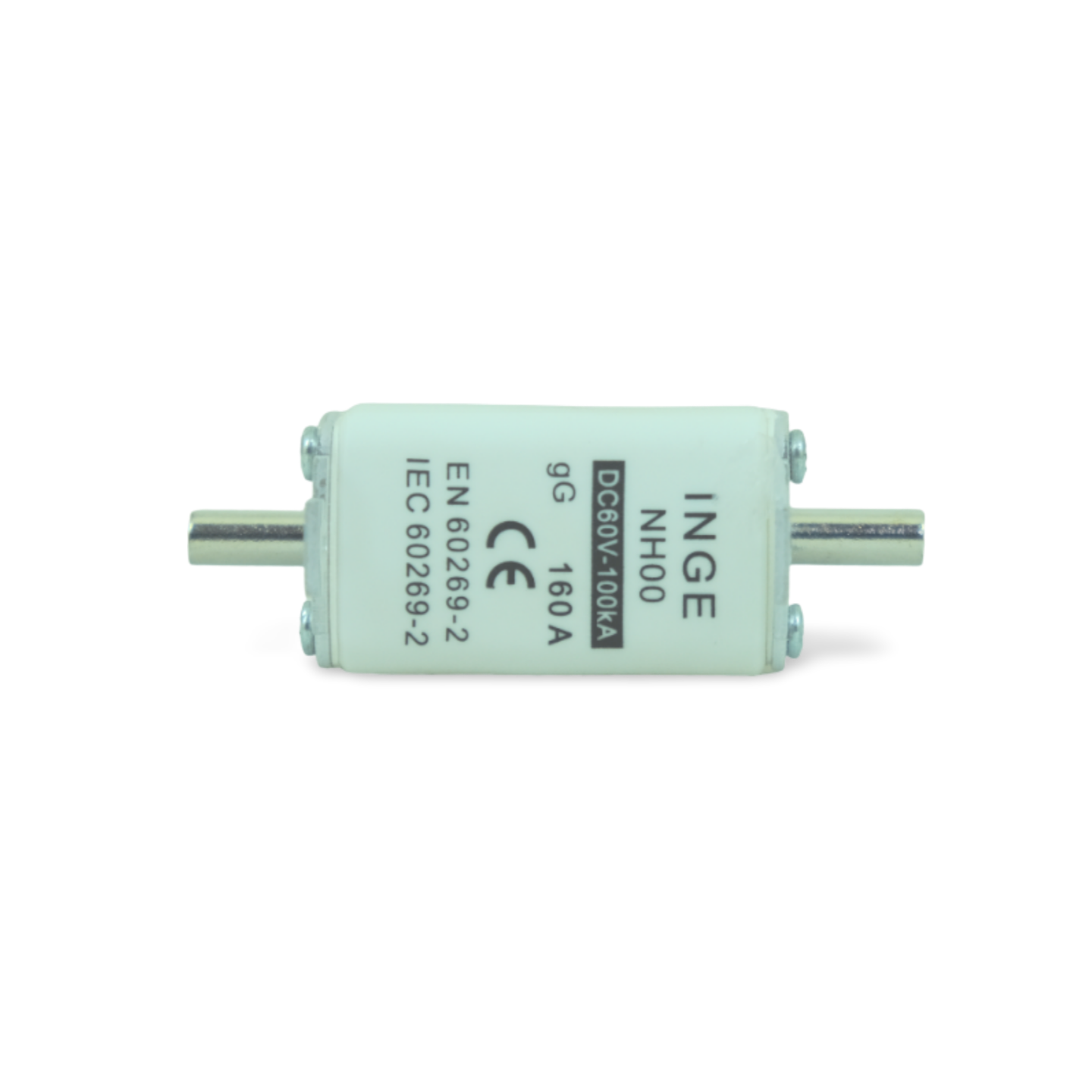
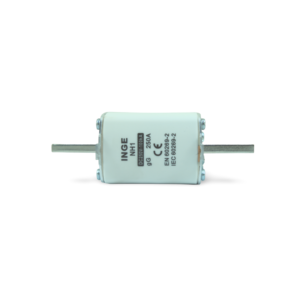
NH fuses, also known as gG fuses (general use), are a type of high-capacity fuse commonly used in industrial and commercial electrical systems. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their construction and features based on the information provided:
Construction of NH Fuses:
- Ceramic Casing:
- NH fuses are housed in a rectangular ceramic casing. This ceramic casing provides insulation and mechanical protection to the fuse element inside.
- Cover Plate:
- The ceramic casing is enclosed by a cover plate at each end. These cover plates typically feature metal blade-style terminals. These terminals serve as connection points for the fuse within the electrical circuit.
- Fuse Element:
- Inside the ceramic casing, there is a fuse element. This element is designed to melt and break the circuit when excessive current flows through it (overcurrent condition). The fuse element is connected to the metal blade terminals on the cover plates.
- Trip Indicator:
- Many NH fuses are equipped with a trip indicator. This indicator visually shows whether the fuse element has blown (melted). It helps quickly identify which fuse in a panel or installation has operated due to an electrical fault.
- Extraction Lug:
- Each cover plate includes a metal extraction lug. This lug is designed to facilitate the removal of the fuse from its holder. It allows for easy extraction when using a NH fuse puller tool, which is the recommended method to safely remove NH fuses from their holders.
Key Features and Uses:
- Industrial and Commercial Applications: NH fuses are widely used in industrial and commercial electrical installations where high-current protection is required.
- Trip Indicator: The trip indicator provides visual feedback, aiding maintenance personnel in troubleshooting electrical faults quickly.
- Safety and Convenience: The design with extraction lugs and dedicated puller tools ensures safe and efficient fuse replacement and maintenance.
Summary:
NH fuses are robust, high-capacity fuses with a ceramic casing and metal blade terminals. They are essential components in electrical systems where reliable overcurrent protection is necessary. Their construction ensures durability, safety, and ease of maintenance, making them suitable for demanding industrial and commercial applications.